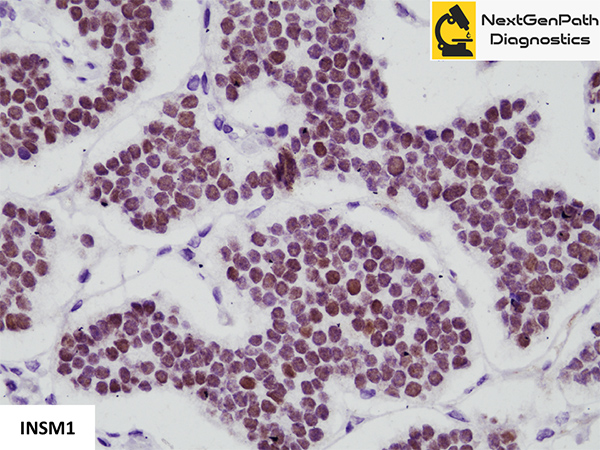
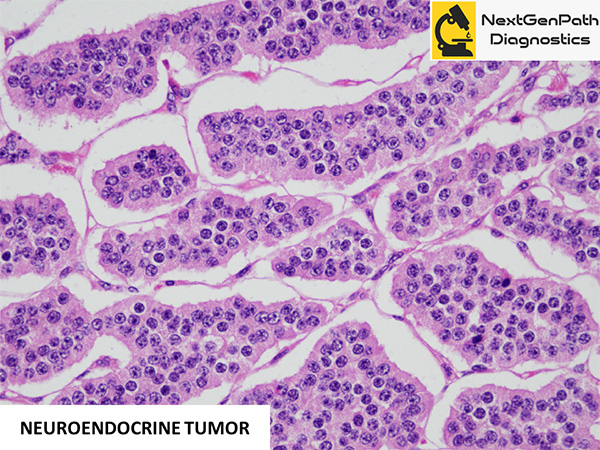
Insulinoma-associated protein 1
- Insulinoma-associated protein 1 (INSM1) is a sequence-specific DNA-binding transcriptional regulator that plays a key role in neurogenesis and neuroendocrine (NE) cell differentiation during embryonic and/or fetal development and encoded by the intronless INSM1 gene.
- INSM1 mRNA is abundantly expressed in fetal NE developmental tissues and normal adult neuroendocrine tissues (adrenal medulla, pineal gland, pituitary gland, gastrointestinal enterochromaffin cells, pancreatic islet cells, thyroid C cells) and developing neurons.
- INSM1 protein is a nuclear marker and its expression by immunohistochemistry has been demonstrated in NE tumors, such as small cell lung cancer (SCLC), pituitary tumors, medullary thyroid carcinoma, merkel cell carcinoma, olfactory neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma, GI and pancreatic NETs, etc.
- As an individual neuroendocrine marker, INSM1 has shown an increased sensitivity and specificity compared to other NE biomarkers (chromogranin A, synaptophysin and CD56) in lung cancer specimens.
- In addition, INSM1 immunostain has a very high negative predictive value.
- INSM1 immunostain is also positive in extraskeletal myoxid chondrosarcoma.
- High expression of INSM1 in SCLC is associated with increased progression free survival and chemosensitivity.
- Apart from its utility in the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors of breast and invasive carcinomas of breast with neuroendocrine differentiation, luminal type B invasive breast cancers with INSM1 expression are associated with significantly better survival.
References
- Bellizzi AM. Immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms: what can brown do for you? Hum Pathol. 2020;96:8-33.
- Yoshida A, Makise N, Wakai S et al. INSM1 expression and its diagnostic significance in extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma. Mod Pathol. 2018;31:744-752.
- Sakakibara R, Kobayashi M, Takahashi N et al. Insulinoma-associated protein 1 (INSM1) is a better marker for the diagnosis and prognosis estimation of small cell lung carcinoma than neuroendocrine phenotype markers such as chromogranin A, synaptophysin, and CD56. Am J Surg Pathol. 2020;44:757-764
- Razvi H, Tsang JY, Poon IK. INSM1 is a novel prognostic neuroendocrine marker for luminal B breast cancer. Pathology. 2020:S0031-3025(20)30888-6.