Hereditary diffuse gastric carcinoma
- Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) is an autosomal dominant cancer syndrome characterized by the
lifetime risk of development of Laurén’s diffuse-type gastric carcinoma (DGC) and lobular breast carcinoma.
- Germline mutation of Cadherin-1 (CDH1), the gene encoding E-cadherin, was detected in 30% to 50% of HDGC patients.
- The International Gastric Cancer Linkage Consortium (IGCLC) proposed clinical criteria to facilitate the screening of individuals with CDH1 germline mutation (pathogenic variant of CDH1).
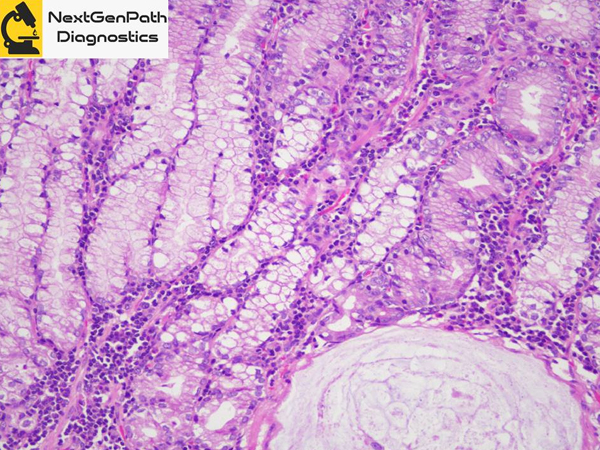
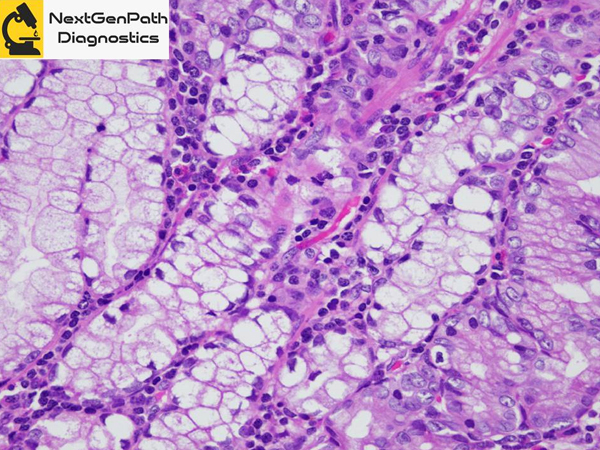
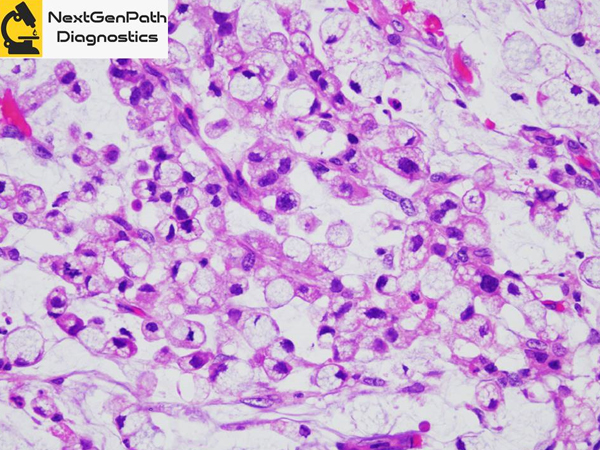
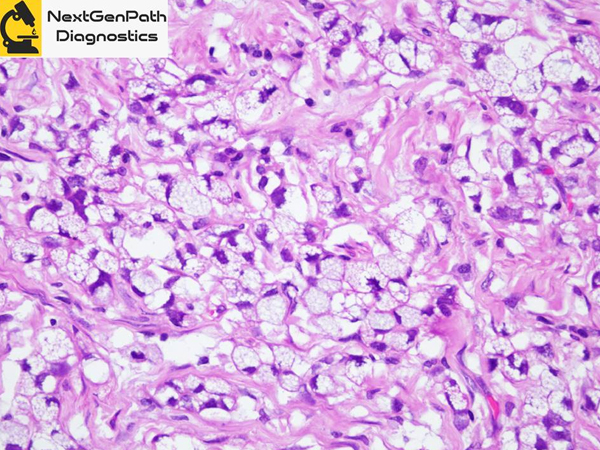
- Signet-ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) in situ (SRCC-pTis) has been reported as a characteristic lesion in HDGC cases with CDH1 germline mutations (CDH1 pathogenic variant), and a precursor of conventional intramucosal SRCC (SRCC-pT1a).
- Histologically, tumor cells of SRCC-pTis are found between normal foveolar epithelial cells and the basement membrane, following a typical pagetoid spread pattern.
- Immunohistochemically, E-cadherin expression is most often lost in SRCC-pTis
- SRCC-pTis is a distinct histologic feature with high specificity for HDGC cases with CDH1 germline mutations.
References
- Tsugeno Y, Nakano K, Nakajima T, et al. Histopathologic Analysis of Signet-ring Cell Carcinoma In Situ in Patients With Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. 2020;44:1204-1212.